Is Blockchain Secure? Understanding Data Protection in Web3

Is Blockchain Secure? Today, online transactions are more crucial than ever before. Due to the rise of cyberattacks and data breaches, protecting sensitive data and transactions has become increasingly important. It is hoped that blockchain technology will provide a solution to these concerns. But is blockchain really secure?
Let’s explore blockchain, its evolution, and how it provides security in the digital age.
What Is Blockchain and How Does It Work?
In a blockchain, transactions are recorded across multiple computers in a decentralized, transparent, and immutable manner. Data manipulation and fraud are reduced by this distributed system, which prevents a single entity from controlling the entire blockchain.
Blockchain transactions are verified by a network of nodes (computers), each holding a copy of the ledger. Because blockchains are decentralized, altering any data requires changing all subsequent blocks, which is nearly impossible.
Cryptographic hashing is at the heart of blockchain security. Blockchain transactions are secured using cryptographic algorithms that produce unique hashes. When data in a block is altered, the hash changes, indicating that the data has been tampered with.
Additionally, blockchain uses consensus protocols (like Proof of Work and Proof of Stake) to ensure that all parties involved agree on the validity of a transaction, further enhancing its security.
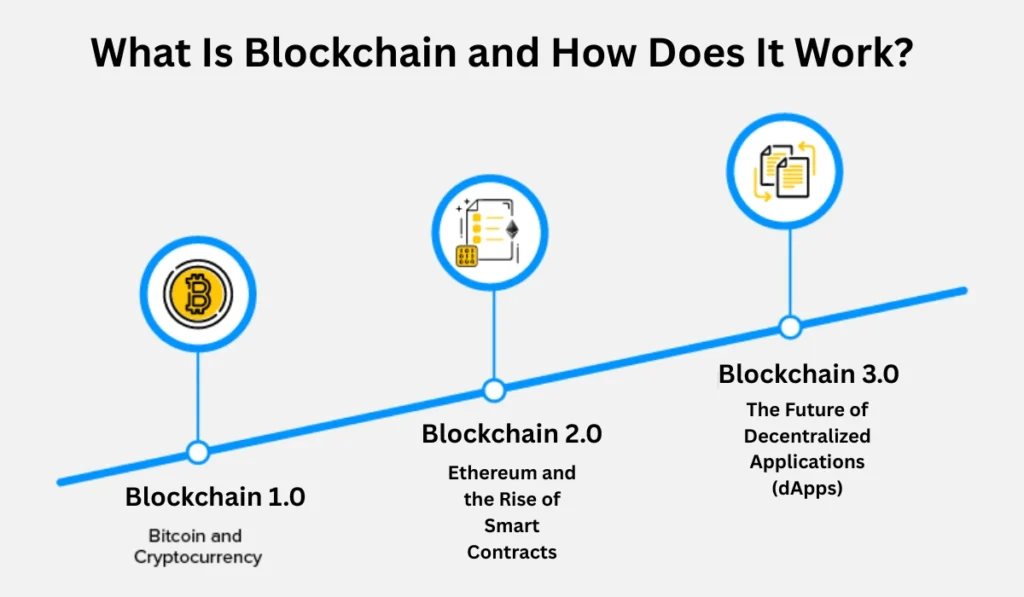
Blockchain 1.0 — Bitcoin and the Birth of Cryptocurrency
The journey of blockchain began in 2008 when an anonymous figure or group known as Satoshi Nakamoto introduced the concept of Bitcoin. Bitcoin’s blockchain was created to provide a decentralized financial system, eliminating the need for third-party institutions like banks.
This was achieved by using a Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanism, where miners solve complex mathematical problems to verify transactions.
While Bitcoin brought the world’s first cryptocurrency, it also highlighted the limitations of blockchain technology, such as scalability and high energy consumption due to PoW. Despite these issues, Bitcoin’s security is considered highly reliable, thanks to its immense computational power and decentralized nature.
Related Read: What is Web3? How It’s Changing the Internet in 2025
Blockchain 2.0 — Ethereum and the Rise of Smart Contracts
In 2014, Ethereum introduced an upgrade to blockchain technology. Vitalik Buterin, a young cryptocurrency enthusiast, saw the limitations of Bitcoin’s blockchain and created Ethereum to address scalability issues while enabling smart contracts.
These contracts automatically execute actions once predefined conditions are met, such as transferring ownership of assets or processing payments, without the need for intermediaries.
Ethereum also introduced Proof of Stake (PoS). This more energy-efficient consensus mechanism allows holders of cryptocurrency to validate transactions based on the amount they hold rather than solving computational puzzles. While PoS is more sustainable, it still maintains the integrity and security of the blockchain.
Blockchain 3.0 — The Future of Decentralized Applications (dApps)
Blockchain 3.0 was designed to solve the scalability, interoperability, and cost-effectiveness issues faced by previous versions. The introduction of Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) allowed for faster processing of transactions, with all applications processed on a single block.
This led to the development of Layer 2 solutions that operate on top of existing blockchains to offer instant, low-cost transactions.
Blockchain 3.0 also brought about the creation of dApps — decentralized applications that run on blockchain networks rather than centralized servers. These applications are more secure because a single entity does not control them, and their data is stored on the blockchain, ensuring transparency and security.
Blockchain’s Security Features: Why It’s Considered Safe
In blockchain, no single party controls the entire system because it operates on a decentralized network. It is therefore difficult for hackers to manipulate data from a single point.
- Cryptographic Hashing: Each transaction is hashed using a unique cryptographic algorithm, and any changes to the transaction would alter the hash, making the tampering easily detectable.
- Immutability: Once a transaction is added to the blockchain, it cannot be changed. This ensures that data remains tamper-proof and provides a permanent record of all transactions.
- Consensus Protocols: Blockchain uses consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work and Proof of Stake, which ensure that all participants in the network agree on the validity of transactions before they are added to the blockchain.
- Transparency and Auditability: Blockchain provides transparency by allowing anyone to view the ledger. This ensures accountability and makes it easier to audit transactions.
Is blockchain Security can be hacked?
Despite its inherent security, blockchain is not completely immune from attacks. In contrast to the technology itself, it is the human element that poses the greatest vulnerability. A few potential risks are listed below:
- Private Key Theft: If a user’s private key (used to sign transactions) is stolen, the attacker could gain control of their cryptocurrency. This highlights the importance of secure storage and management of private keys.
- Smart Contract Bugs: Blockchain applications, especially decentralized applications (dApps), rely on smart contracts. If these contracts are poorly written or contain bugs, they can be exploited by hackers.
- 51% Attacks: In public blockchains, if an attacker gains control of more than 50% of the network’s mining power, they could theoretically manipulate the blockchain. However, this is much harder to achieve in large networks like Bitcoin.
- Exchange and Wallet Hacks: While blockchain itself is secure, cryptocurrency exchanges and wallets can be vulnerable to hacks, as seen in the infamous Mt. Gox incident. Users must ensure they use trusted platforms and maintain secure practices.
Conclusion: Is Blockchain Secure
By design, blockchain technology provides a high level of security due to cryptographic algorithms, decentralization, and consensus protocols that ensure data integrity and prevent tampering. There are, however, risks associated with any technology.
Ultimately, the security of blockchain depends on how it is implemented, how users manage their private keys, and how developers write and test smart contracts.
The security features of blockchain technology will improve as it evolves, addressing scalability issues, reducing energy consumption, and becoming even more secure. However, as with any digital technology, users should follow best practices when managing their private keys and be aware of phishing attacks and software vulnerabilities.
With its security, transparency, and decentralization, blockchain has the potential to revolutionize industries. Security must be prioritized by both technology and users in order to realize the full potential of this technology.






